



Next: Discussion
Up: The Kriging Estimator
Previous: Minimum Estimation Variance
Contents
Both kriging systems can be easier expressed in matrix form. Let denote
 the ``kriging matrix''
the ``kriging matrix''
and
 and
and  , two vectors,
, two vectors,
then the kriging system gets the simple form
which, in the case of invertibility of the matrix  , immediately provides
the solution for
, immediately provides
the solution for
 :
:
The expression of the kriging variance becomes
where
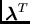 denotes the transposed vector
of
denotes the transposed vector
of
 .
.
Rudolf Dutter
2003-03-13
![]() the ``kriging matrix''
the ``kriging matrix''

